You can use constants that apply to specific single- and - phase voltages to calculate current (I) and kilowatts (kW). Three - phase circuits distribute electrical power along multiple conductors in the same power line. The current waveform of each conductor is offset in time from the others.
Electrical - phase equations. With single-phase AC power there is only one single sinusoidal voltage.
One - phase induction motor is running, voltage=41 current=0.
How to calculate motor efficiency and torqu.
The product of the voltage and current is the apparent power and measured in VA (or kVA). Helpful tools for calculating motor loads with formulas. At 4volts, a - phase motor draws 1. At any speed of the blower, the . To Find Amperes when HP is known: Single Phase.
To find Amperes when KW is known: Single Phase.
The synchronous speed of an induction motor depends on the frequency of the power supply and on the. AC three phase amps to kilowatts calculation. Calculation with line to line voltage . BHP = Break Horsepower ( Motor ) r = running np = nameplate.
Motor sheave = Existing Motor sheave Dia.
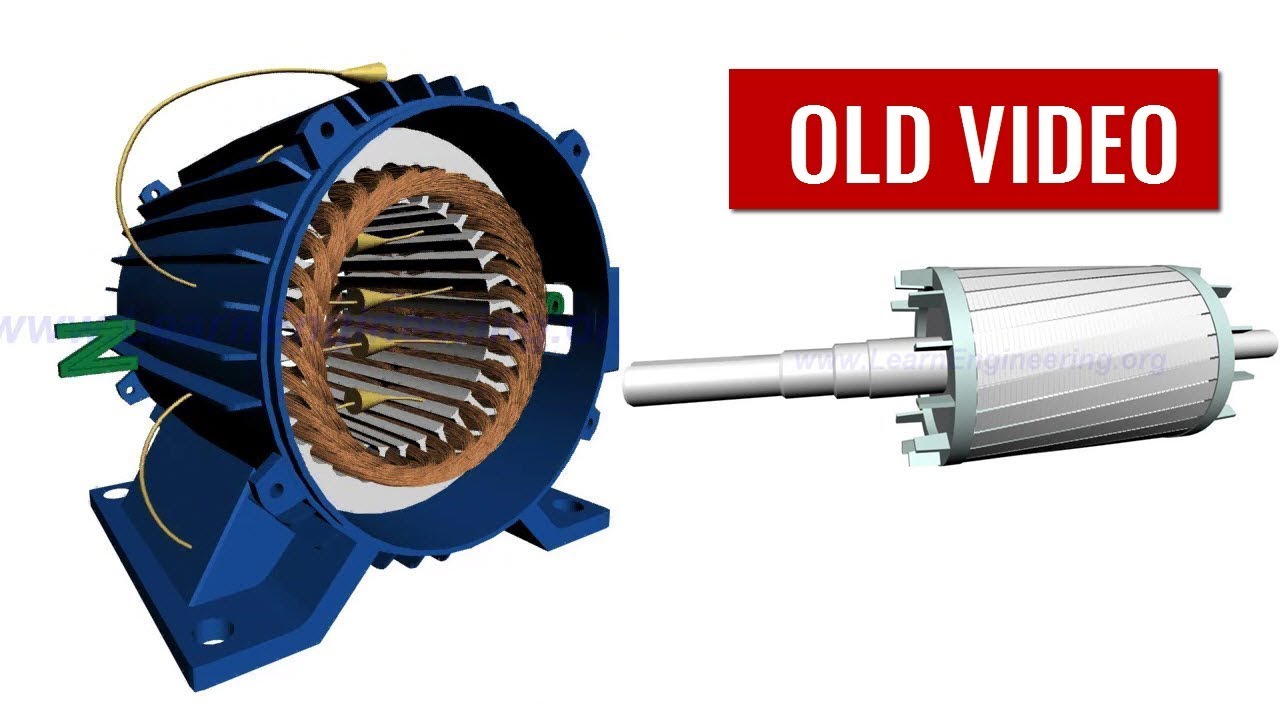
Firstly the magnitude of rotor current, secondly the flux which interact with the rotor of three phase induction motor and is responsible for producing emf in the rotor part of induction motor , lastly the power factor of rotor of the three phase induction motor. Combining all these factors together we get the equation of torque as- . These Static Phase Converters Will Convert Single Phase1VAC, 2VAC, 4VAC or 6VAC Input Power To Three Phase Output Power For Motor. All of this information pertains to Squirrel Cage type ACthree phase induction motors.
The calculators below can be used to calculate electric motor amps, horsepower and - phase kVa. Definition three - phase electrical motors power factor.
Example :- unit induction motor power rated hp,2VAC, phase , power factor,calculated the full load ampere. Enter real power in kilowatts (kW). For three phase , select voltage type.
The power factor correction capacitor should be connected in parallel to each phase load. The Synchronous speed can be calculated as follows: 1times the frequency (F), divided by the number of poles .
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.